ABSTRACT
The Internet of Things is built based on various sensors and networks. Sensors for stereo capture are essential for acquiring information and have been applied in different fields. In this paper, we focus on the camera modeling and analysis, which is very important for stereo display and helps with viewing. We model two kinds of cameras, a parallel and a converged one, and analyze the difference between them in vertical and horizontal parallax.
Even though different kinds of camera arrays are used in various applications and analyzed in the research work, there are few discussions on the comparison of them. Therefore, we make a detailed analysis about their performance over different shooting distances. From our analysis, we find that the threshold of shooting distance for converged cameras is 7m. In addition, we design a camera array in our work that can be used as a parallel camera array, as well as a converged camera array and take some images and videos with it to identify the threshold.
CAMERA ARRAY MODELS
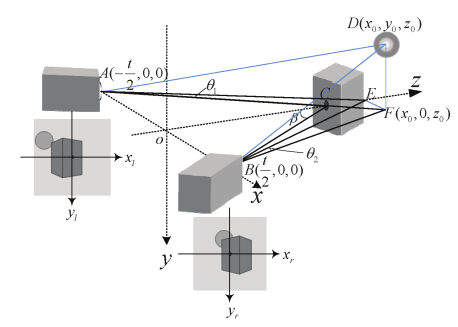
Figure 1. Camera array schematic diagram
We build a simplified converged model, as Figure 1 shows. A and B are the optical center of the two cameras. C is a reference object, which lies on the z axis, and AC, BC are the cameras’ optical axes. D is the target object, which we want to display. F is the projection of object D on the x − z plane. E is the point that F projects on the z axis, so EF//OA. According to the geometry, Equation can be obtained, where L indicates convergence distance, t indicates the distance between A and B and β represents the converged deflection angle.
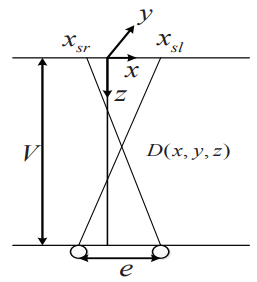
Figure 2. Stereopsis diagram
For a point (x,y,z) on a stereo image in the image coordinate system and a view distance V (seen in Figure 2), we can obtain the following relationship based on the human eye imaging characteristics.
AUTO-CONVERGED CAMERA ARRAY REALIZATION
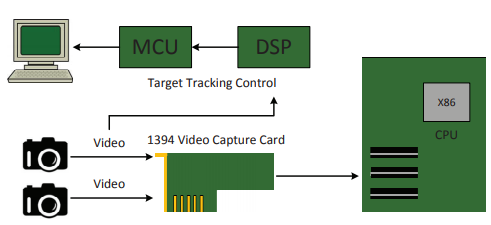
Figure 6. Component interconnections
An experimental test-bed was configured using multimedia PC components, Microcontroller Unit (MCU) and Digital Signal Processor (DSP). A diagram of the sensor, date acquisition and processing components is shown in Figure 6. The multimedia 1394 video capture card can be used to grasp 1024 × 768 pixel color images from either camera. Image processing and camera control are performed in real-time on the DSP and MCU.

Figure 7. The physical diagram of the auto-converged camera array
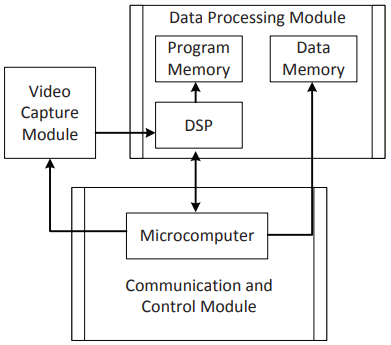
Figure 8. Structure of the system hardware
As shown in Figure 7, the system consists of the video capture module, the data processing module and the communication and control module. Figure 8 shows the physical frame of the designed auto-converged camera array. Auto-converged arrays are widely used in three-dimensional reconstructions, face recognition, gesture recognition and image assessment based on stereo vision, and so on. In image assessment, stereo images are necessary for the experiments. Auto-converged camera arrays can be a perfect tool to take stereo images for the study of image assessment, as Yang et al. do in.
AUTO-CONVERGED EXPERIMENT AND MEASURE
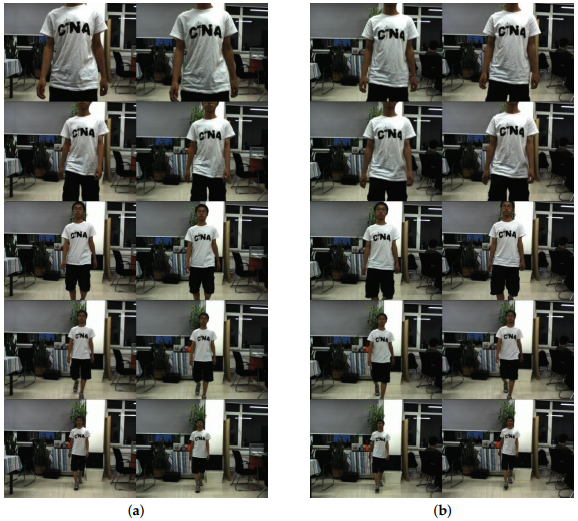
(a) Images taken by using the converged camera array; (b) images taken by using the parallel camera array.
In order to verify the analysis above, we use a parallel and a converged camera array to shoot images of a moving man as the target in the same condition, then contrast these two groups of images, as shown in Figure 9. The resolution of the camera array used is 1024 × 768. The convergence distance varies in the range of 1m to 10m.
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we build a parallel camera array model and a simplified converged camera array model as the base of subsequent analysis. A physical camera array is developed, which can be used as a parallel array, as well as a converged array. This is convenient for the different choices according to the real needs. The pros and cons of these two kinds of cameras are discussed. A conclusion is that converged arrays are more suitable for short-distance shooting and parallel arrays for long-distance shooting. Our work can be guidance to the application of the camera arrays in different environments. For future work on the auto-converged camera array, we need to focus on camera calibration and visual stereo-video evaluation.
Source: Tianjin University
Authors: Jiachen Yang | Ru Xu | Zhihan Lv | Houbing Song