ABSTRACT
A compact annular ring microstrip antenna was proposed for a wireless sensor network (WSN) application in the 2.4 GHz band. In this paper the major considerations of the conformal antenna design were the compact size and the impact on antenna’s performance of a steel installation base. By using a chip resistor of large resistance (120 Ω ) the antenna size was reduced to 38% of that a conventional annular ring patch antenna.
With the addition of the steel installation base the resonant frequency of the antenna increases about 4.2% and the bandwidth reduces from 17.5% to 11.7% by adjusting the load resistance simultaneously. Several key parameters were discussed and optimized, and the antenna was fabricated and its performance measured. The antenna is well matched at 2.4 GHz with 34.2 dB return loss and –2.5 dBi peak gain. Meanwhile, it exhibits excellent radiation patterns with very low cross-polarization levels.
ANTENNA CONFIGURATION AND DESIGN
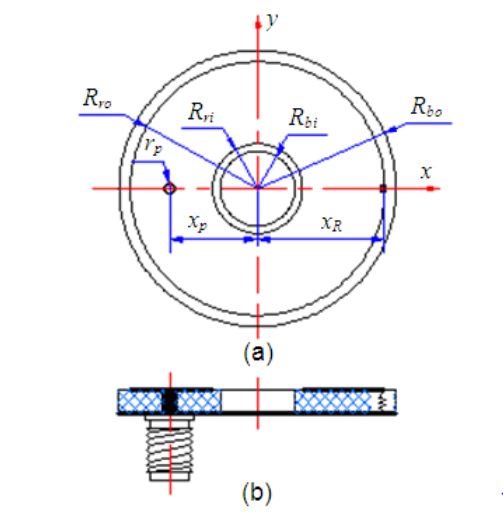
Figure 2. Configuration and parameters of the proposed antenna. (a) Top view. (b) Cross section
The schematic of the antenna configuration is show n in Figure 2. It was designed as an annular ring structure with outer radius of Rbo (≤ 20 mm), inner radius of Rbi (≥ 5 mm), and thickness of h. To reduce costs FR4 substrate with relative dielectric constant of εr = 4.5 and loss tangent of tan δ = 0.02 was selected.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
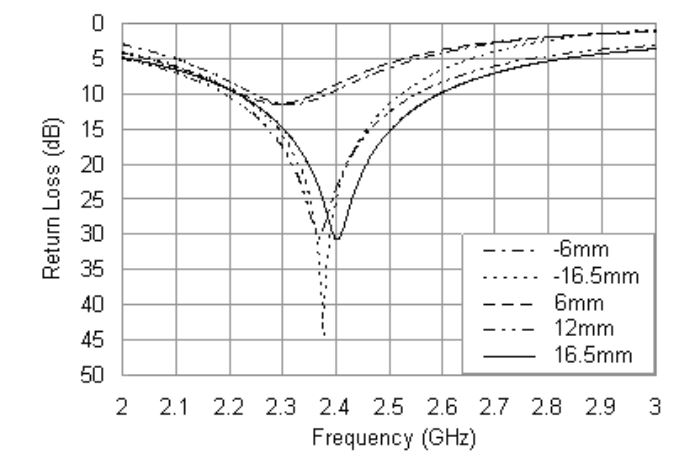
Figure 4. Simulated return loss curves with different values of xR
As seen from Figure 4, the case of loading at the inner edge of the patch can result in a further reduction in resonant frequency, which corresponds to an even larger size reduction at a given opera ting frequency. In this case, the resistor loading has maximum effects on the resonant-frequency lowering due to the surface current has a maximum value around the inner edge of the patch, however, the matching level is poor.
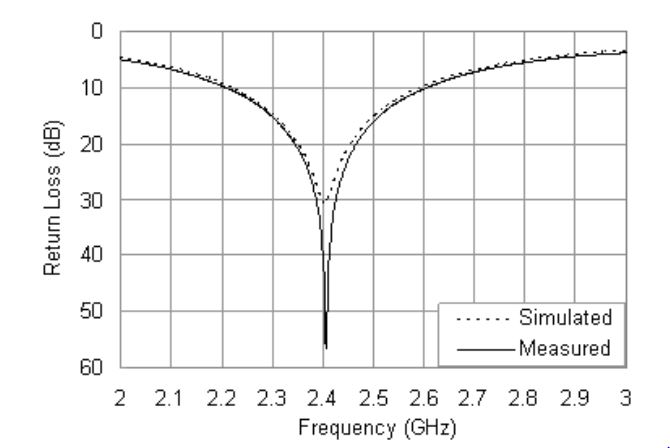
Figure 7. Measured and simulated return loss curves
The only variation between the fabricated prototype and the simulation model was the mounting method of the resistor, and the following results showed that the influence of the variation was negligible. The measured and simulated return loss curves are compared in Figure 7. Both the measured and simulated curves are excited at 2.4 GHz with return loss as 56.7 and 30.8 dB, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a compact annular ring mirostrip antenna backed with a steel installation base was realized. By using a loading resistor of large resistance, 38% miniaturization is achieved compared with a conventional annular ring antenna. It is also found that the steel installation base has a great influence on the antenna’s characteristics. With the addition of the steel installation base, the resonant frequency of the antenna increases about 4.2%, while the measured bandwidth was reduced from 17.5% to 11.7% by simultaneously optimizing the load resistance.
The realized antenna is well matched at 2.4 GHz with good radiation characteristics. It should also be noted that, due to the dramatic size reduction and influences of the steel installation base, the radiation efficiency reduces from 24.9% to 12.7% and the peak gain is –2.5 dBi. The configuration of proposed antenna is simple and easy to fabricate. Several antennas have been used in the WSN successfully and the performance has been verified. The design provides a reasonable solution to the applicability of microstrip antenna used in narrow spaces.
Source: North University
Authors: Daihua Wang | Linli Song | Hanchang Zhou | Zhijie Zhang
>> Project Report on Microstrip Patch Antenna Design for Final Year Students