ABSTRACT
Nowadays, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing technology that allows to integrate digital devices into a network. Using the IoT technology to collect information from a variety of Internet connected GNSS receivers provides a unique opportunity to obtain real-time information about the special and temporal distribution of ionospheric characteristics with high resolution. The ability to create a dense sensor network is achieved through the usage of cheap single-frequency GNSS receivers based on the Arduino technology.
This approach can be implemented to obtain real-time data on the total electron content (TEC) of the ionosphere. The determination of the ionospheric delay of the radio signal of GLONASS/GPS satellite and the calculation of the ionospheric TEC are carried out directly in the GNSS receiver. The results are transmitted over a wireless communication channel via Internet to a cloud server, where maps of the TEC of the ionosphere are constructed.
EXPERIMENTS
- Methods
- Technologies
Methods
The determination of the ionospheric TEC by a single-frequency navigation receiver is based on the processing of code and phase pseudorange measurements on the same carrier frequency. The method is based on finding the difference between two successive measurements of pseudoranges, measured by the code and phase of the carrier frequency of the radio signal.
Technologies
To create special low-cost devices for implementaion single-frequency method of ionospheric TEC monitoring is possible with the help of the Arduino technology. This is an open programmable hardware platform based on the use of printed circuit boards with a microcontroller. To create a ground-based receiver, a GNSS module is connected to the card that has access to the Internet via a wireless WiFi network. The determination of the ionospheric delay of the radio signal and the calculation of the ionospheric TEC are carried out directly in the GNSS receiver.
Recently, the technology of “Internet of Things” (IoT) is actively developing. IoT is a reliable network of devices, with built-in electronics, software and sensors. IoT technology allows one to transmit TEC data over a wireless communication channel, independently process them without requiring human help.
RESULTS
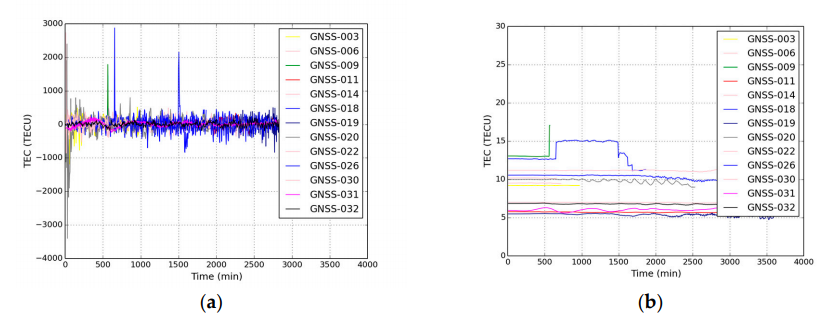
Figure 1. Results of TEC measurements by single-frequency method
(a) Before Kalman filtering; (b) After Kalman filtering.
In the case of processing the total electron content of the ionosphere, the Kalman filter takes into account errors in the accuracy of measurements of the range to the receiver and the variability of the values of the TEC, minimizing the RMS measurement error. Figure 1a shows the distribution of the total electron content as a function of time. Figure 1b shows a graph of the change in the TEC of the ionosphere over time, which has been filtered by Kalman using a standard mathematical apparatus.
DISCUSSION
The main task of GNSS is the determination of the coordinates of the receiver processing radio signals from navigational satellites. The full deployment of GNSS and the improvement of algorithms for solving inverse problems of remote sensing significantly improved the methods for determining ionospheric parameters. Global monitoring helps to keep a record of the current state of the ionosphere.
The use of technology IoT to gather information from multiple GNSS receivers connected to the Internet, gives one the unique opportunity to obtain operational information about the distribution of TEC with high spatial resolution. The ability to create a dense measuring network is achieved through the creation of cheap GNSS receivers. The determination of the ionospheric delay of the radio signal and the calculation of the ionospheric TEC are carried out directly in the GNSS receiver. The results are transmitted over a wireless communication channel through the global Internet to a dedicated server, where maps of the TEC of the ionosphere.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of technology IoT to gather information from multiple GNSS receivers connected to the Internet, gives one the unique opportunity to obtain operational information about the distribution of TEC with high spatial resolution. The results are transmitted over a wireless communication channel through the Internet to a cloud service, where maps of the TEC of the ionosphere can be constructed.
Source: Russian State Hydrometeorological University
Authors: Olga Lazareva | Vladimir Chukin
>> Top IoT Projects using Arduino for Final Year ECE/EEE Students
>> Top IoT Projects using Microcontroller for ECE Students
>> 50+ IoT based Wireless/GSM Projects for Engineering Students
>> IoT Software Projects for Students